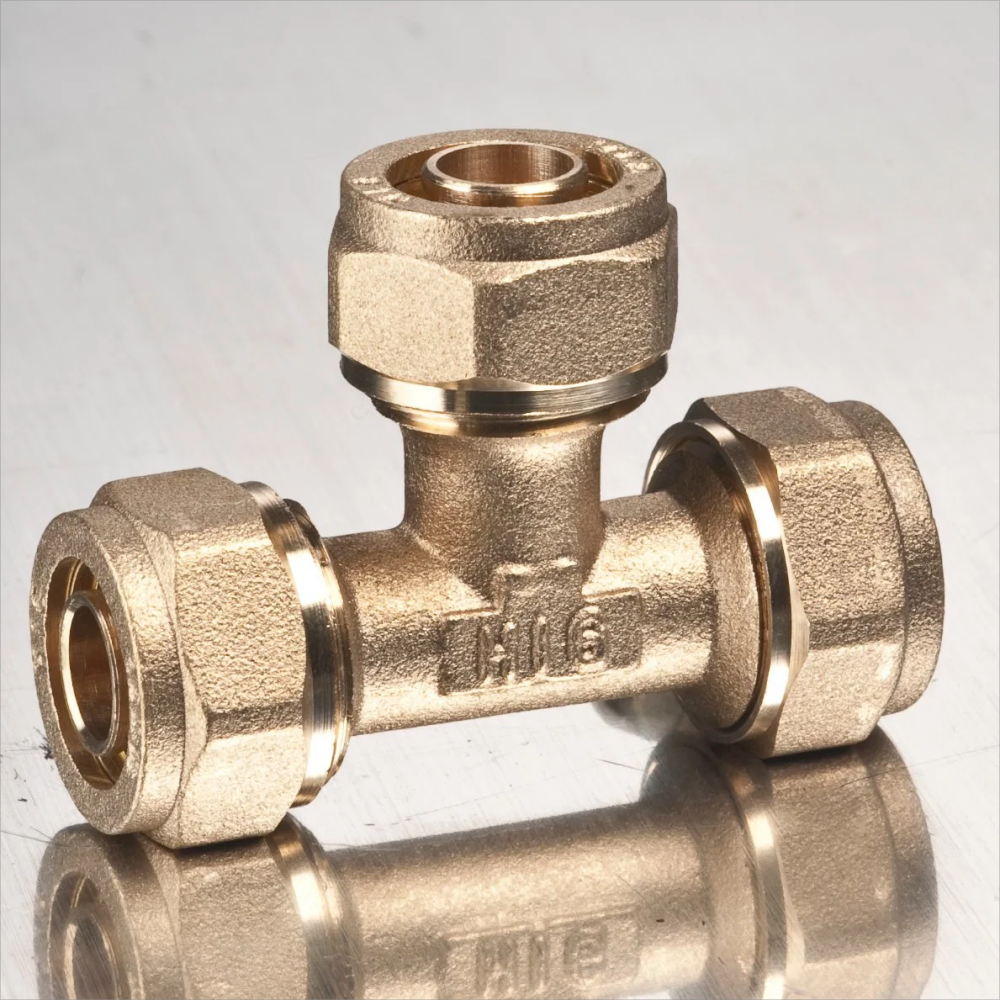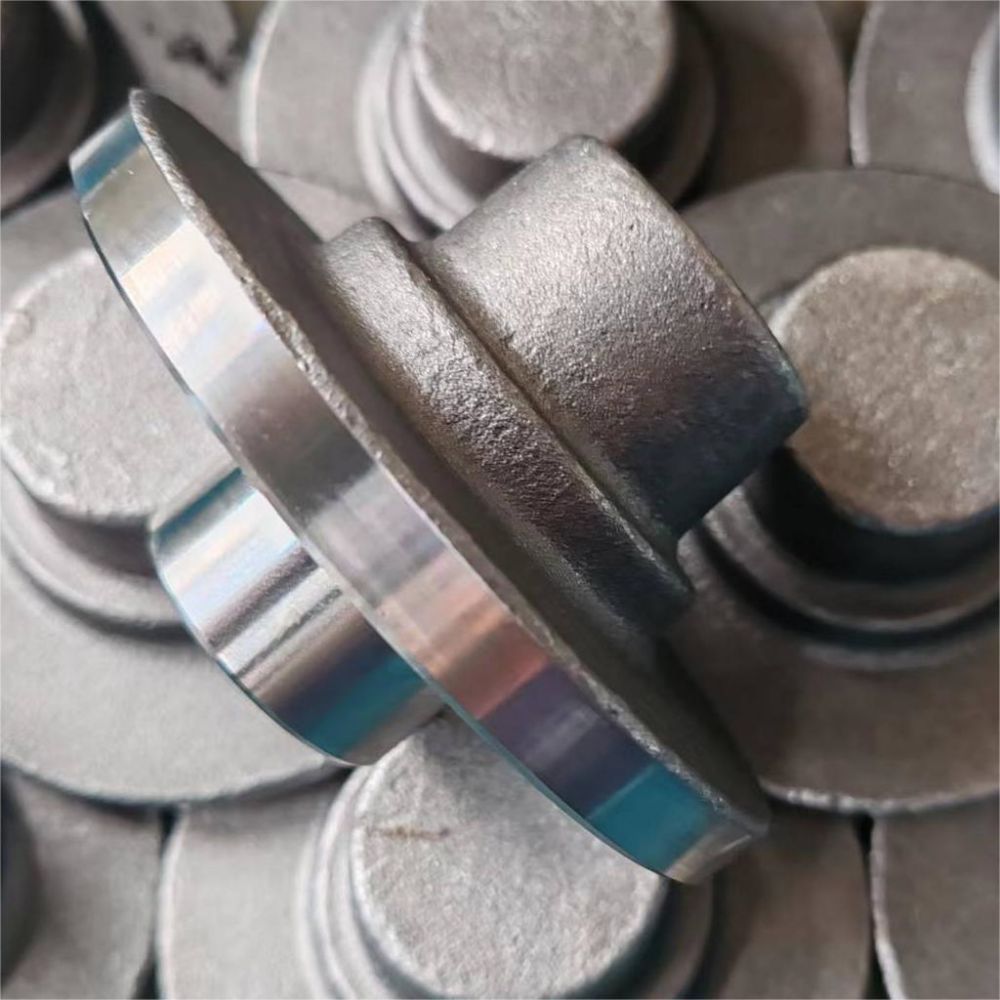
What is Impact Extrusion
Impact extrusion is a highly efficient manufacturing technique used to produce various products. Which is one of the fastest ways to get to near-net shape for many parts and components. Our process begins with a lubricated metal slug—also called a blank or a puck—that is placed in a die cavity. The metal puck is struck with a punch powered by a mechanical or hydraulic press. This forces the metal to flow into a shape or position almost instantly. In this post, we will cover its working principles, materials used, surface treatments available, advantages, disadvantages, applications, and future trends.
How impact extrusion works?
Impact extrusion is a manufacturing process used to create hollow metal parts with thin walls. Here’s a detailed look at how it works:

Types Of Impact Extrusion

Reverse Impacting
In reverse-impact extrusions, metal flows backwards—in the opposite direction in which the force is applied—and then around the punch. The resultant part has a shape similar to that of the punch.

Forward Impacting
In forward impact extrusions, the punch pushes the material through an aperture inside the die. The punch fits into the cavity to the point that the metal cannot flow backward.

Combination Impacting
Combination Impacting is the combination of two impacting processes. Making more complicated shapes for parts Combination impacting pushes metal through a hole and as well backward around the punched.
The Basics of Impact Extrusion
Impact Extrusion is a precise and efficient machining process that produces high-quality cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool. This technology is crucial in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, due to its ability to create intricate and accurate components.
1. Material Placement
The process begins with a slug or blank of metal, typically a soft, ductile material like aluminum, copper, lead, zinc, or tin. This slug is placed in a die, a tool that shapes the material.
2. Punch Movement
A punch, a solid piece of metal, then strikes the slug at high speed and pressure. The impact force is usually generated by a mechanical or hydraulic press.
3. Metal Flow
Upon impact, the metal flows around the punch and into the die cavity, taking the shape of the die. The metal’s flow is primarily in the radial direction, allowing the material to spread thinly and evenly.
4. Die Action
The die, which is precisely machined to the desired shape of the final product, confines and directs the flow of the metal. Depending on the die design, the process can create various shapes, including cylindrical, conical, or complex profiles.
5. Ejection
After the punch retracts, the newly formed part is ejected from the die. This step may involve additional mechanical systems to ensure the part is removed without damage.
The Basics of Impact Extrusion
Several factors affect the quality and efficiency of the impact extrusion process:
- Temperature
Although impact extrusion is generally a cold-working process (performed at room temperature), the temperature of the material can influence its ductility and flow characteristics. Preheating the metal can sometimes be beneficial, especially for harder materials.
- Pressure and Speed
The pressure exerted by the punch and the speed at which it strikes the slug are critical. Higher pressures and faster speeds typically result in better material flow and more precise shapes but require robust machinery and tooling.
- Lubrication
To minimize friction and prevent damage to the die and punch, lubrication is often applied to the slug and die surfaces. This also helps in the smooth ejection of the final part.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Impact Extrusion
Ventajas

Preparation:
Fast production rates.

Material Utilization:
Minimal waste compared to other methods.
Low Cost:
Economical for large-scale production.
Precision:
High dimensional accuracy and consistency.
Disadvantages

Equipment Investment:
Requires significant initial capital.

Material Requirements:
Only certain metals are suitable.

Limited Scope:
Best for specific shapes and sizes.
Materials For Impact Extrusion
Material selection is crucial for the success of the impact extrusion process. The choice of material affects the ease of extrusion, the quality of the final product, and the range of possible applications. Here, we will discuss the common materials used in impact extrusion, their characteristics, and typical grades or alloys.

Characteristics:
- Lightweight
- High ductility
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good thermal and electrical conductivity
Common Grades/Alloys:
- 1100: Commercially pure aluminum, known for its excellent ductility and corrosion resistance. Ideal for applications requiring good formability.
- 3003: An alloy with manganese, providing better strength than 1100 while maintaining good formability and corrosion resistance.
- 6061: A heat-treatable alloy with magnesium and silicon, offering good mechanical properties and weldability. Suitable for applications requiring higher strength.
Characteristics:
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity
- High ductility
- Good corrosion resistance
Common Grades/Alloys:
- C11000 (Electrolytic Tough Pitch Copper): High electrical conductivity, used in electrical and electronic components.
- C12200 (Phosphorized Copper): Enhanced corrosion resistance and weldability, used in plumbing and heating systems.
- C14500 (Tellurium Copper): Improved machinability while maintaining good electrical conductivity, used in electrical connectors and contacts.
Characteristics:
- High density
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low melting point
- Good malleability
Common Grades/Alloys:
- Pure Lead: Used in applications requiring high density and radiation shielding.
- Lead-Antimony Alloys: Enhanced hardness and strength, used in battery grids and radiation shielding.
- Lead-Tin Alloys: Improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, used in soldering and bearing applications.
Characteristics:
- Good corrosion resistance
- High ductility
- Low melting point
- Economical
Common Grades/Alloys:
- Zamak 3: A zinc-aluminum alloy with excellent casting properties and good mechanical strength. Used in die-casting applications.
- Zamak 5: Similar to Zamak 3 but with higher copper content for improved strength and hardness. Used in automotive and hardware components.
- Zinc-Aluminum Alloys (ZA-8, ZA-12): Higher aluminum content for better strength and hardness, used in precision components.
Characteristics:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good biocompatibility
- High melting point
Common Grades/Alloys:
- Grade 1: Pure titanium, offering excellent corrosion resistance and formability. Used in chemical processing and marine applications.
- Grade 2: Pure titanium with good strength and ductility, widely used in industrial applications.
- Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V): An alloy with aluminum and vanadium, providing high strength, light weight, and good corrosion resistance. Used in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance engineering applications.
Surface Treatment in Impact Extrusion
Surface treatment is a vital aspect of the impact extrusion process, significantly affecting the performance, durability, and appearance of the final product. Proper surface treatment can enhance properties such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics. Here, we will explore the importance of surface treatment, common methods, and their impact on product performance.
Importance of Surface Treatment
Surface treatment is crucial for several reasons:
- Enhances Durability: Increases resistance to wear and tear, extending the product’s lifespan.
- Improves Corrosion Resistance: Protects against environmental factors, preventing rust and degradation.
- Optimizes Surface Properties: Improves hardness, reduces friction, and enhances conductivity.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Provides a polished, uniform appearance, improving the product’s marketability.
- Functional Performance: Enhances specific properties required for the product’s application, such as electrical conductivity or reflectivity.
Common Surface Treatment Methods

Mechanical Polishing
- Purpose: To smooth the surface and improve its appearance.
- Process: Involves abrasive techniques to remove surface irregularities and achieve a mirror-like finish.
- Applications: Used for products requiring a high-gloss finish, such as consumer goods and decorative items.

Chemical Treatment
- Purpose: To clean and prepare the surface for further processing.
- Process: Involves using acids, alkalis, or other chemicals to remove oxides, scale, and contaminants.
- Applications: Pre-treatment for plating or coating processes, ensuring better adhesion and uniformity.

Electroplating
- Purpose: To deposit a thin layer of metal onto the surface.
- Process: Involves using an electrolytic solution to deposit metals such as chromium, nickel, or gold onto the product.
- Applications: Used in electronics, automotive, and jewelry for enhanced corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetics.

Shot Peening
- Purpose: To improve fatigue strength and resistance to stress-corrosion cracking.
- Process: Involves bombarding the surface with small spherical media to induce compressive residual stresses.
- Applications: Used in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery components to enhance durability.

Anodizado
- Purpose: To increase the thickness of the natural oxide layer on the surface.
- Process: An electrochemical process that enhances corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing the surface in various colors.
- Applications: Commonly used for aluminum products in the aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics industries.

Powder Coating
- Purpose: To apply a protective and decorative coating.
- Process: Involves applying a dry powder to the surface and curing it under heat to form a durable finish.
- Applications: Widely used in the automotive, appliance, and furniture industries for a high-quality, long-lasting finish.

Passivation
- Purpose: To enhance corrosion resistance.
- Process: Involves treating the surface with a nitric or citric acid solution to remove free iron and form a passive oxide layer.
- Applications: Used for stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant alloys in medical and food processing equipment.
Surface Treatment Impact on Product Performance

- Wear Resistance
Surface treatments like electroplating and anodizing can increase the wear resistance of products used in harsh environments, making them more resilient in such conditions as corrosion.
- Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion-resistant treatments such as anodizing, passivation, and powder coating provide crucial corrosion protection to products subjected to extreme environments.
- Aesthetics
Aesthetics Mechanical polishing, anodizing, and powder coating enhance the aesthetic value of products to make them more desirable to consumers.
- Functional Properties
Electroplating with metals like gold or silver enhances electrical conductivity, essential for electronic components.
Anodizing can improve thermal conductivity and emissivity, beneficial for heat dissipation applications.
Choosing the appropriate surface treatment depends on several factors:
- Material Type: Different materials respond differently to surface treatments. For example, aluminum is commonly anodized, while steel might be electroplated or powder coated.
- Application Requirements: Consider the specific performance needs such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic requirements.
- Cost and Production Volume: Some surface treatments are more cost-effective for large production volumes, while others may be better suited for smaller, high-value items.
- Environmental Considerations: Eco-friendly processes and materials are increasingly important in modern manufacturing.
Applications of Impact Extrusion
Impact extrusion is a versatile manufacturing process used across various industries due to its ability to produce high-quality, lightweight, and complex metal parts. Here, we explore the specific applications of impact extrusion in different sectors:

Electronics Industry

Packaging Industry

Medical
and Pharma-ceutical Industry

Consumer Goods

Energy Industry
- Industria del automóvil
- Industria aeroespacial
- Electronics Industry
- Packaging Industry
Components:
- Engine Parts: Cylinders, pistons, and valve lifters are often produced using impact extrusion due to the need for high strength and precise tolerances.
- Heat Exchangers: The process is ideal for creating thin-walled tubes and fins used in radiators and intercoolers.
- Brackets and Supports: Lightweight yet strong components that support various systems within the vehicle.
Benefits:
- Weight Reduction
- Strength and Durability
- Precision
Components:
- Structural Parts: Frames, ribs, and stiffeners used in aircraft fuselage and wings.
- Landing Gear Components: Strong and lightweight parts that need to withstand high-impact forces.
- Heat Shields and Panels: Thin-walled components used in thermal protection systems.
Benefits:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
- Corrosion Resistance
- Precision Manufacturing
Components:
- Enclosures and Housings: Cases for electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
- Connectors and Contacts: Precision parts used in electrical connectors and interconnects.
- Heat Sinks: Efficiently dissipate heat from electronic components.
Benefits:
- Thermal Management
- Miniaturization
- Aesthetic and Functional Finishes
Components:
- Metal Cans and Containers: Beverage cans, aerosol cans, and food containers.
- Tubes: Collapsible tubes for products such as toothpaste, creams, and gels.
Benefits:
- Seamless Construction
- High-Speed Production
- Recyclability
- Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
- Consumer Goods
- Energy Industry
Components:
- Medical Devices: Housings and components for devices such as inhalers, insulin pens, and surgical instruments.
- Implants: Structural components for orthopedic implants and dental implants.
Benefits:
- Biocompatibility
- Precision and Cleanliness
- Customizability
Components:
- Sporting Goods: Components for items like golf clubs, fishing reels, and bicycle frames.
- Appliances: Structural and functional parts for household appliances.
- Tools: Durable and lightweight hand tools and power tool components.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Performance
- Durability
- Aesthetic Appeal
Components:
- Battery Housings: Casings for lithium-ion and other batteries used in electric vehicles and portable electronics.
- Heat Exchangers: Components for systems in power plants and renewable energy installations.
- Fuel Cells: Parts used in hydrogen fuel cells and other energy generation devices.
Benefits:
- Efficiency
- Reliability
- Customization

Let's Start Project!
We will give you a quick reply and quote within 12 hours.
- Phone: 0086-18779223927
- Email: Lynnyao@prototekparts.com
- Address: Nanchang,Jiangxi,China


























































