What is CNC Turning
CNC turning, a fundamental aspect of modern manufacturing, is a versatile and efficient process for creating precision parts. it is a sophisticated machining process with versatility, rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool. CNC Turning produces an intricate and accurate understanding of this process’s basics and key components, highlighting its significance in modern times.
How CNC Turning Works?
CNC Turning is a precise and efficient machining process that produces high-quality cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool. This technology is crucial in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, due to its ability to create intricate and accurate components.
The Basics of CNC Turning
CNC Turning is a precise and efficient machining process that produces high-quality cylindrical parts by rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool. This technology is crucial in various industries, from automotive to aerospace, due to its ability to create intricate and accurate components.

Preparation:
Programming: A CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the part is created and converted into a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) program. This program generates G-code, which the CNC machine reads to control its movements.
Setup: The workpiece is securely clamped onto the lathe’s spindle. The cutting tools are installed in the tool turret or holder, ready for machining.

Machining:
Rotation: The lathe’s spindle rotates the workpiece at high speeds.
Cutting: The cutting tool moves along the workpiece’s surface, following the programmed path. The tool can move in multiple axes (typically X and Z axes) to create the desired geometry.
Material Removal: As the cutting tool engages the workpiece, it removes material in the form of chips, shaping the workpiece into the specified design.

Completion and Inspection:
Finishing Operations: Additional processes like threading, knurling, or drilling may be performed if required.
Inspection: The finished part is measured and inspected to ensure it meets the specified tolerances and quality standards.
The Basics of CNC Turning
A CNC Turning system comprises several critical components that work together to achieve precise machining:

Control Unit: The control unit, or CNC controller, interprets the G-code and controls the machine’s movements and operations.
Spindle: The spindle holds and rotates the workpiece. Its speed can be adjusted based on the material and desired surface finish.
Cutting Tools: Various cutting tools are used in CNC Turning, each designed for specific operations such as roughing, finishing, threading, and parting off.
Tool Turret/Holder: This component holds multiple tools and can index them into position as needed for different machining operations.
Servo Motors: These motors drive the movement of the machine’s components with high precision, ensuring accurate positioning and smooth operation.
Types Of CNC Turning
There are a variety of CNC turning operations that CNC lathes that are possible to perform on a live lathe in a CNC turning factory. These include Parting, Hard turning Facing, Boring Reaming, Taper turn, threading, drilling, Knurling, Grooving, etc. It is available in various tools, costs, and setup times.
1. Tapered turning: make an elongated part that has its diameter decrease between one and the other.
2. Hard turning: is suitable for materials that have a Rockwell C hardness greater than 45. It is typically done after the heat treatment.
3. Spherical generation: make a spherical-finished surface rotating around a fixed axis of rotation.
4. Facing: is a turning process involving the workpiece being turned to its center.
5. Parting: Create deep grooves to separate an entire or partial component from its stock.
6. Grooving: like a parting but cut only to a specified depth either from the outside or inside of the workpiece.
7. Drilling: Remove the drill bits from the workpiece’s interior by holding the drill bits stationary within the lathe’s tailstock or the tool turret. Boring: increase the size or smooth out an existing hole.
8. Knurling: Cut serrated patterns on the surface of the piece using a knurling tool to alter or improve the visual impact as well as a handgrip.
9. Reaming: Take some of the materials from a drilled hole to ensure that the diameter is precise.
10. Threading: Threads: turn threads of screw that are non-standard and standard generally refers to single-point threading.
11. Polygonal turning: non-circular forms of machine operation that do not interrupt the motion of raw materials.
Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC Turning is a widely used machining process known for its precision, efficiency, and versatility. Understanding its key features helps highlight why it is a preferred method in various industries for producing high-quality cylindrical parts. This article will explore the essential features of CNC Turning, emphasizing its capabilities and advantages.

Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC Turning is a versatile machining process that can handle various materials, making it suitable for multiple industries and applications. The choice of material significantly impacts the machined parts’ performance, durability, and functionality.
This article will explore the common materials used in CNC Turning, their properties, and typical applications.
Common Materials Used in CNC Turning
- Proprietà: Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, consumer electronics housings, medical devices, and machinery parts.
- Proprietà: High strength, durability, toughness, available in various grades with different properties (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, tool steel).
- Applications: Structural components, automotive parts, machinery, tools, and equipment.
- Proprietà: Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, durability, and good temperature resistance.
- Applications: Medical devices, food processing equipment, chemical processing equipment, marine components, and kitchen appliances.
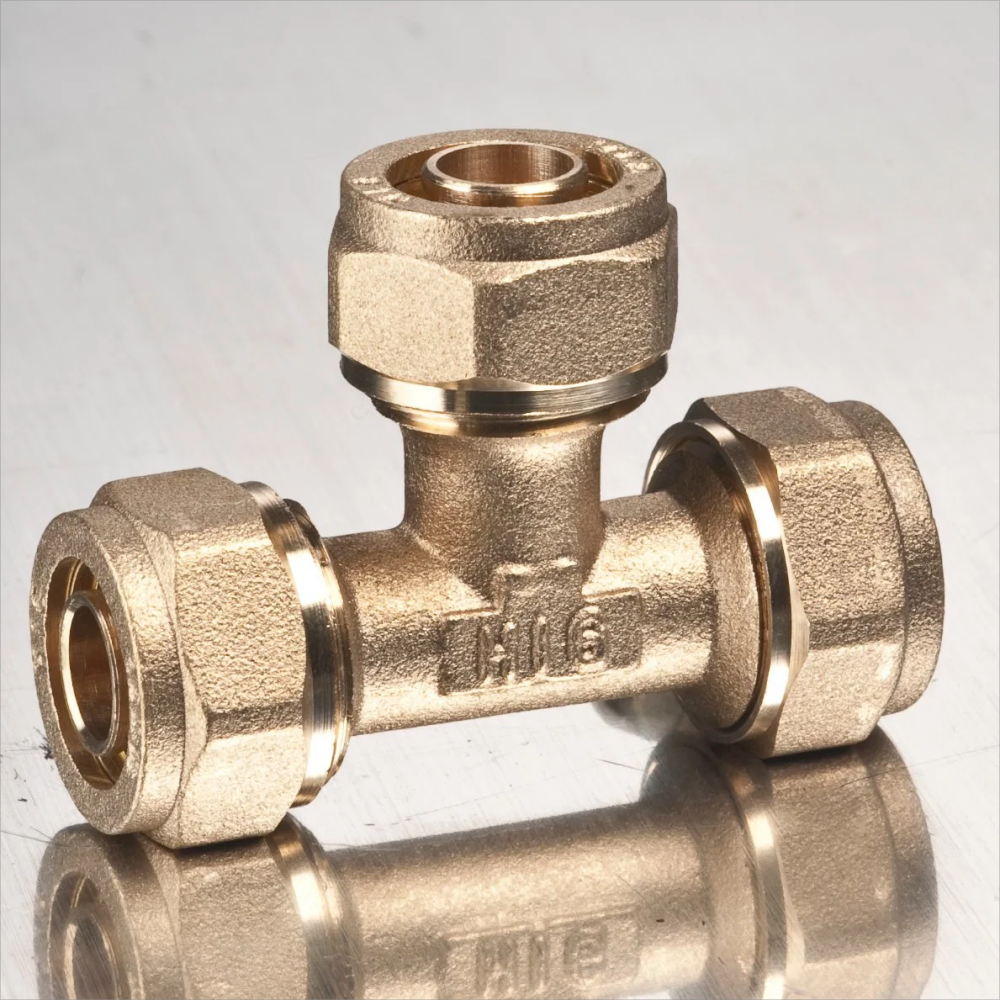
- Proprietà: Good machinability, corrosion resistance, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, attractive appearance.
- Applications: Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings, decorative hardware, and musical instruments.
- Proprietà: Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, good corrosion resistance, malleability.
- Applications: Electrical components, heat exchangers, plumbing, and decorative items.
- Proprietà: High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, high melting point.
- Applications: Aerospace components, medical implants, military applications, and high-performance automotive parts.
- Proprietà: Extremely lightweight, good machinability, moderate strength, good thermal conductivity.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, portable electronics, and sporting goods.
Finish in CNC Turning
Finishment is a critical step in the CNC turning process that enhances machined parts’ appearance, physical properties, and durability. This article will explore common surface treatment methods used in CNC Turning, their applications, and their benefits.
Common Finish Methods

1.Polishing
Purpose: Polishing aims to improve surface smoothness and aesthetics by reducing surface roughness.
Methods:
- Mechanical Polishing: Uses abrasive materials and polishing tools to remove surface irregularities through mechanical friction.
- Chemical Polishing: Involves using chemical solutions to dissolve micro-roughness on the surface.
- Electrochemical Polishing: Combining electrical and chemical processes to smoothen the surface by removing a thin layer of material.
Applications: Used for parts requiring high gloss and low surface roughness, such as automotive trim, consumer electronics housings, and high-end furniture fittings.

2.Electroplating
Purpose: Electroplating forms a metallic coating on the part surface to enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and electrical conductivity.
Methods:
- Nickel Plating: Increases corrosion resistance and hardness.
- Chrome Plating: Enhances wear resistance and provides a decorative finish.
- Copper Plating: Improves electrical conductivity, often used for electrical connectors.
- Gold Plating: Increases conductivity and oxidation resistance, commonly used in high-end electronics.
Applications: Widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device industries.

3.Anodizing
Purpose: Anodizing is primarily used for aluminum and its alloys, creating an oxide layer on the surface to enhance corrosion resistance, hardness, and aesthetics.
Methods:
- Standard Anodizing: creates a uniform oxide layer, improving corrosion resistance and hardness.
- Hard Anodizing: Forms a thicker and harder oxide layer, suitable for high-wear applications.
- Colored Anodizing: Adds dyes during the anodizing process to achieve various colors on the surface.
Applications: Used for aerospace components, consumer electronics housings, architectural materials, and bicycle parts.

4.Coating
Purpose: Coatings can enhance corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and appearance. Common coating methods include powder coating and spray coating.
Methods:
- Powder Coating: Electrostatic spray is used to apply powdered paint, which is then cured under heat to form a durable protective layer.
- Liquid Spray Coating: Applies liquid paint cured naturally or through baking to form a coating.
- PVD Coating: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) deposits a thin film on the surface, offering high hardness and wear resistance.
Applications: Suitable for various industrial equipment, automotive parts, household appliances, and sports equipment.
Purposes and Benefits of Surface Treatment

Enhancing Corrosion Resistance
Surface treatments form protective layers that prevent parts from corroding in harsh environments, extending their lifespan. Electroplating and anodizing significantly enhance material corrosion resistance.

Increasing Hardness & Wear Resistance
Some treatments, such as hard anodizing and PVD coating, significantly increase surface hardness, reducing wear and extending part life.

Improving Appearance
Surface treatments enhance the aesthetics of parts, making them more marketable. Polishing, electroplating, and colored anodizing are commonly used for high-decorative-value parts.

Boosting Product Performance
Specific treatments can improve part performance, such as electroplating for better conductivity, coating for reduced friction, and anodizing for better surface insulation, meeting particular application needs.
- Finish in CNC Turning plays a vital role in modern manufacturing. Different surface treatment methods offer various advantages, and the appropriate treatment choice depends on specific application requirements and material characteristics. Proper surface treatment can enhance the appearance and performance of parts, ensuring their stability and longevity under various conditions.
Application Markets for CNC Turning
CNC Turning is a versatile machining process used across a wide range of industries. Its ability to produce high-precision, complex parts makes it essential in various application markets. This section explores the primary markets where CNC Turning is utilized, highlighting specific applications and the benefits it brings to each sector.

Industria automobilistica
The automotive industry is one of the largest consumers of CNC Turning services. The precision and efficiency of CNC Turning make it ideal for producing various automotive components.
- Engine Components: CNC Turning is used to manufacture engine parts such as pistons, cylinders, crankshafts, and camshafts. These components require high precision to ensure proper engine performance and efficiency.
- Transmission Parts: Gears, shafts, and other transmission components are turned to exact specifications to ensure smooth operation and longevity.
- Suspension and Steering: Precision-turned parts like steering knuckles, tie rods, and suspension components contribute to vehicle stability and handling.
- Custom Parts and Prototypes: CNC Turning is also used for producing custom automotive parts and prototypes for new vehicle designs.

Industria aerospaziale
The aerospace industry demands the highest levels of precision and reliability due to the critical nature of its applications. CNC Turning meets these stringent requirements.
- Aircraft Engine Parts: Components such as turbine blades, shafts, and housings are turned with high precision to withstand extreme conditions and stresses.
- Structural Components: CNC Turning produces lightweight, strong parts like brackets, struts, and fasteners used in aircraft structures.
- Landing Gear: Precision-turned components ensure the reliability and safety of landing gear systems.
- Spacecraft Components: Parts used in satellites, rockets, and space probes require the highest standards of accuracy and durability.

Medical Devices
The medical device industry relies heavily on CNC Turning to produce high-precision components essential for patient care and safety.
- Surgical Instruments: Scalpels, forceps, and other surgical tools are manufactured with exacting precision to ensure their effectiveness and safety.
- Implants: CNC Turning produces components for implants such as hip joints, knee joints, and dental implants, which must meet stringent biocompatibility and accuracy requirements.
- Diagnostic Equipment: Parts for MRI machines, CT scanners, and other diagnostic devices are turned to precise specifications to ensure accurate results.
- Prosthetics: Custom prosthetic components are manufactured using CNC Turning to meet individual patient needs.

Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics market demands high-precision, aesthetically pleasing components that CNC Turning can deliver.
- Housings and Enclosures: CNC Turning is used to manufacture sleek, precise housings for smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other electronic devices.
- Connectors and Adapters: Small, intricate connectors and adapters are turned to ensure reliable electrical connections.
- Cooling Components: Heat sinks and other cooling components are turned to exact specifications to manage the heat generated by electronic devices.
- Custom Parts: Prototypes and custom parts for new electronic designs are produced efficiently with CNC Turning.

Industrial Machinery
Industrial machinery and equipment often require robust, precise components that can be produced using CNC Turning.
- Pumps and Valves: CNC Turning manufactures components for pumps and valves, ensuring they operate reliably under various conditions.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Precision-turned parts like cylinders, pistons, and fittings are essential for the proper functioning of hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- Gears and Bearings: High-precision gears and bearings are turned to ensure smooth operation and longevity in industrial machinery.
- Tooling and Fixtures: CNC Turning produces custom tooling and fixtures for manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.

Other Industrial Applications
CNC Turning is also used in various other industrial applications, providing precision and efficiency across different sectors.
- Oil and Gas: Components such as drill bits, valve parts, and pipeline fittings are turned to meet the demanding conditions of the oil and gas industry.
- Renewable Energy: CNC Turning manufactures parts for wind turbines, solar panel mounts, and other renewable energy systems.
- Agriculture: Precision-turned components are used in agricultural machinery, ensuring reliability and efficiency in farming operations.
- Marine: CNC Turning produces parts for marine engines, propulsion systems, and other equipment used in the maritime industry.
CNC Turning is a crucial technology in modern manufacturing, offering precision, efficiency, and versatility across a wide range of application markets. From automotive and aerospace to medical devices and consumer electronics, CNC Turning plays a vital role in producing high-quality components essential for various industries. Its ability to meet stringent requirements and produce complex parts ensures its continued relevance and growth in the manufacturing sector.
Prototek provides top-tier CNC turning services characterized by precision, accuracy, and speed. We excel in manufacturing intricate parts with stringent tolerances, utilizing a broad spectrum of materials, including exotic alloys and plastics. Our team of seasoned machinists and engineers leverages cutting-edge equipment and software to ensure consistent quality and timely delivery for every project. Additionally, we offer value-added services such as design consultation, material selection guidance, and various finishing options to fulfill customer specifications. Prototek is the perfect partner for any CNC turning needs, delivering expert advice, rapid turnaround, and a dedication to excellence.
Let's Start Project!
We will give you a quick reply and quote within 12 hours.
- Phone: 0086-18779223927
- Email: Lynnyao@prototekparts.com
- Address: Nanchang,Jiangxi,China