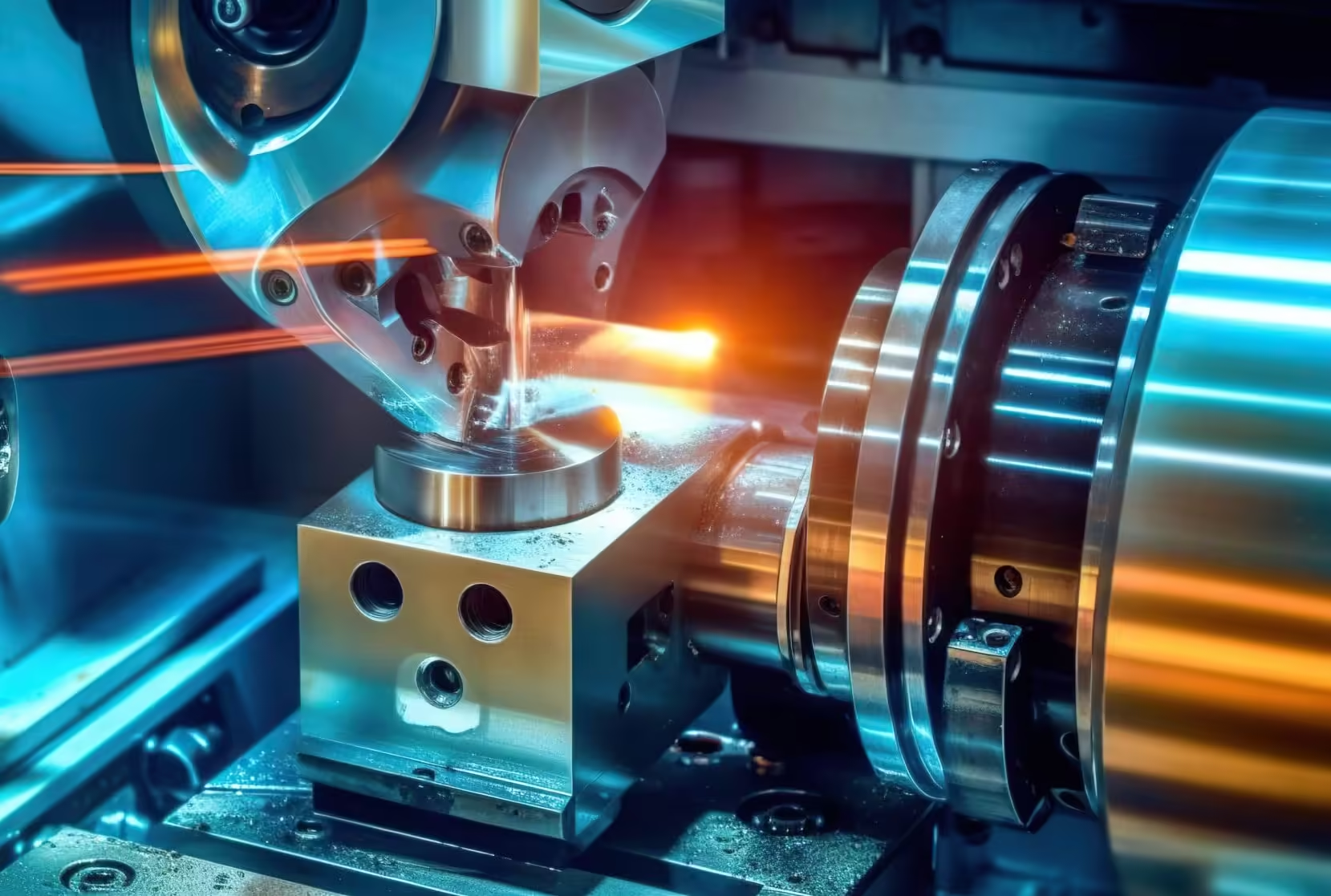
What is CNC Milling
CNC milling is a machining process that utilizes computer numerical control (CNC) machines to remove material from a workpiece. In CNC milling, a rotating cutting tool moves along multiple axes to create complex shapes and features in the workpiece. CNC milling is a crucial manufacturing process used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and more. For producing precision components and parts with high efficiency and accuracy.
How CNC Milling Works?

Design and Programming

Machine Setup

Machining Operations

Coolant and Chip Removal

Quality Control and Finishing
CNC Milling Processes
Utilize a multi-point rotation tool to remove the material from the workpiece. It begins by fixing the block made of plastic or metal in the CNC mill. Utilizing G-code, the CNC tool is programmed to cut out pieces from the material swiftly. material. Basic mills comprise an axis system of three (X, Z, and Y), an extremely well-known and widely-used machining technique. When using 3-axis machining, the workpiece is fixed and the rotating tool can cut along the x and Z three axes. Additionally, modern mills can accommodate two additional axes, while 4-axis CNC machining and 5-axis CNC machining provide more flexibility and are frequently employed to manufacture precision parts.
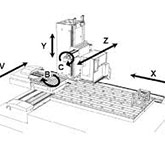
3-Axis Cnc Milling
For 3-axis machining, the tool can move in three distinct directions independently or simultaneously relative to the material. It can move in the X, Y, and Z linear directions, it’s back to front (Y-axis), side to side (X-axis), and up and down (Z-axis).
3-axis machining is great for sheet milling parts like panels and enclosures. It’s often used to make 2D and 2D.5 geometry.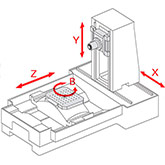
4-Axis Cnc Milling
4-axis machining has the same 3 axes (XYZ) as 3-axis, plus an additional axis for rotation. The B-axis rotates the workpiece about the X-axis. Rotation allows 4 sides to be machined while the part rests in the fixture, and only requires one setup.
More complex geometries, such as arcs and helices, can be achieved more efficiently with 4-axis machining.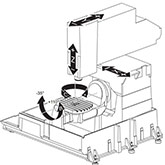
5-Axis Cnc Milling
Consists of three conventional axes and two additional rotary axes. In 5-axis milling, both the workpiece and the spindle rotate, the rotary axes operate independently of each other, and the workpiece is rotated at a certain angle relative to the cutting tool, allowing 5 sides of the workpiece to be machined.
5-axis machining can produce highly complex 3D shapes and curves, allowing manufacturers to make parts that are usually made using molds.Features of CNC Milling
- Benefits
Rapid Turnaround
Using the latest CNC machines, Prototek produces highly accurate, quick-turn parts in as fast as 10 days. We also instantly quote CNC machined parts, cutting days off of your RFQ process.
High Precision Tolerances
Offers high-precision tolerances ranging from +/-0.001″ – 0.005″, depending on customer specs. We are the experts in making parts that are truly custom and ready to use.
Scalabilità
CNC Machining is perfect for prototyping and production parts. Prototek’s massive scale can help you scale up from the testing phase to production runs of 100,000 parts or more.
Custom Surface Finishes
Suitable for many different kinds of substrates, make your parts just the same as real products.
Material Selection
Choose from over 40+ metal materials. CNC Machining offers a wide variety of certified materials.
Cost Saving
Low investment in tooling and preparation costs, economical for parts with simple structure.
- Drawbacks
Material limitations
When machining hard materials (such as hard steel, titanium alloy, etc.), may result in longer processing times and higher costs.
Scale Effect
Unit cost and delivery time are not as good as injection molded parts.
The Metal Materials of CNC Milling?
- Alluminio
- Brass & Copper
- Acciaio
- Titanium Alloys
- 6061-T6: One of the most popular aluminum alloys, known for its good mechanical properties and weldability. Commonly used for automotive parts, aerospace components, and consumer goods.
- 7075-T6: High-strength aluminum alloy, often used in aerospace applications due to its excellent fatigue resistance and strength-to-weight ratio.
- 2024-T3: Known for its high strength and excellent fatigue resistance, commonly used in aerospace structures and military applications.
- 5052-T5: With good corrosion resistance, high plasticity and weldability, and is often used in the fields of ships, automobile parts, building materials, etc.
- 2A12-T2: With good strength and corrosion resistance, and is often used in the aerospace field, such as aircraft structural parts, aircraft wheels, etc.
- C36000 Brass (360 Brass): Known for its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Commonly used in fittings, fasteners, and electrical components.
- C26000 Brass (Cartridge Brass): Has a good combination of strength and ductility, often used in ammunition casings, radiator cores, and hardware.
- C11000 Copper (Electrolytic Tough Pitch, ETP): Highly conductive and malleable, commonly used in electrical applications, heat exchangers, and plumbing.
- C17200 Copper (Beryllium Copper): Known for its high strength, hardness, and electrical conductivity. Used in springs, connectors, and precision instruments.
- 1018 Steel: A low-carbon steel with good weldability and machinability, often used for structural applications.
- 4140 Steel: A chromium-molybdenum alloy steel with high toughness, strength, and wear resistance, commonly used in manufacturing gears, shafts, and other high-stress parts.
- A36 Steel: A standard structural steel grade with good weldability and machinability, often used in construction and structural applications.
- 304 Stainless Steel: The most common stainless steel, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and good formability. Widely used in kitchen equipment, chemical processing, and architectural applications.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Offers superior corrosion resistance compared to 304, especially in marine and chemical environments. Commonly used in medical devices, marine applications, and food processing equipment.
- 17-4 PH Stainless Steel: A precipitation-hardening stainless steel known for its high strength and hardness, often used in aerospace, chemical, and petrochemical industries.
- Grade 2 Titanium: Commercially pure titanium with good corrosion resistance and weldability, often used in chemical processing and marine applications.
- Grade 5 Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V): The most commonly used titanium alloy, known for its high strength, light weight, and excellent corrosion resistance. Commonly used in aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance automotive parts.
How to select the CNC milling material?


Material Strength: Different applications require different levels of material strength. For example, aerospace and automotive components often require high-strength materials like titanium or steel to withstand high stress and load conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: For parts exposed to harsh environments or chemicals, corrosion resistance is crucial. Stainless steel and certain plastics provide excellent resistance to corrosion.
Heat Treatment Characteristics: Some materials, like certain steels, can be heat-treated to enhance their properties, such as hardness and strength, which is essential for specific industrial applications.
Cost and Availability: The material cost and its availability in the market can significantly influence the overall project budget and timeline. Aluminum and certain plastics are generally more affordable and readily available compared to specialized materials like titanium alloys.
Machinability: Ease of machining affects production efficiency and tool wear. Materials like aluminium and brass are easier to machine, while tougher materials like titanium and stainless steel may require specialized tools and techniques.
Surface Treatment
Purposes Of Surface Treatment
The main purposes of surface treatment are to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and aesthetics.This is crucial for extending the service life of parts and meeting specific application requirements.
Common Surface Treatment Methods
To enhance the performance and appearance of CNC-milled parts, surface treatment is often necessary. Common methods include:
Choosing Surface Treatment Methods
The choice of surface treatment should be based on the type of material, application environment, and usage conditions. For example, aluminum parts typically use anodizing, while steel parts may opt for electroplating or spraying.
Don’t see the finish you need? Submit an Quote and we’ll look into a finishing process for you.
Precision
Precision is a key performance indicator in CNC milling, including dimensional tolerance, geometric tolerance, and surface roughness. High-precision machining ensures that parts meet design specifications, ensuring their reliability and performance in assembly and use.
Factors Affecting Precision
CNC milling precision is influenced by various factors, including:
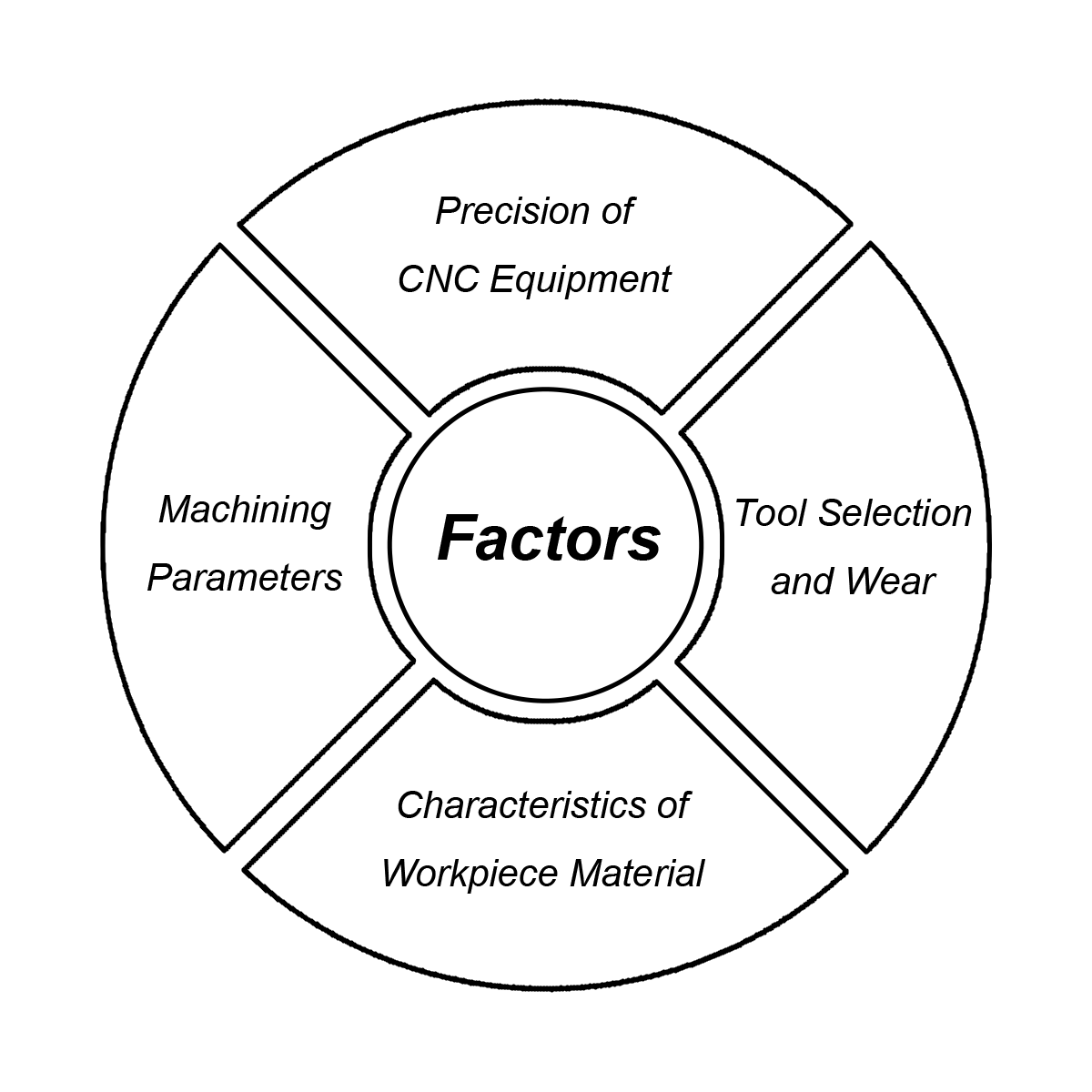
- Precision of CNC Equipment: The mechanical and control precision of the equipment directly affects the machining outcome.
- Tool Selection and Wear: The quality and wear condition of the tools impact machining precision and surface quality.
- Characteristics of Workpiece Material: Different materials’ machining characteristics (e.g., hardness, toughness) affect precision.
- Machining Parameters (e.g., cutting speed, feed rate): These parameters need to be optimized to achieve the best machining results.
Methods to Improve Precision
To enhance CNC milling precision, the following measures can be taken:
Use high-precision CNC equipment

Reglarly maintain and calibrate the equipment

Optimize cutting parameters

Use high-quality tools
Properly design fixtures and jigs
Quality Inspection and Control
High-precision machining requires strict quality inspection and control. Common inspection equipment includes Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and surface roughness testers. Regular quality checks ensure that parts meet design requirements.
Expanded Market Applications
CNC milling is used across a wide range of industries, each with specific material and precision requirements:

Aerospace
It is an invaluable process for producing complex, high-precision components like engine parts, structural elements, and landing gear. Titanium alloys and composite materials like carbon fiber composites tend to offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability when selecting your material of choice for CNC milling applications.

Produzione automobilistica
CNC milling has long been used in the automotive industry to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, and custom interior features. Materials like aluminum and steel tend to provide the right balance of strength and machinability.

Medical Devices
CNC milling is an integral part of manufacturing medical implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic devices. High-precision materials like stainless steel, titanium, and biocompatible plastics such as PEBA are essential to ensure patient safety and device performance.
Electronics
CNC milling is often utilized in the electronics industry to craft precise enclosures, heat sinks, and connectors made of materials like aluminum or certain plastics chosen for their thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and lightweight properties.

Consumer Products
CNC milling allows for the creation of customized parts for consumer products ranging from sports equipment and household gadgets to luxury goods. Using materials ranging from plastics and aluminum to more exotic components like carbon fiber.

Tooling and Prototyping
CNC milling is an increasingly popular means of creating customized tools, molds, and prototypes across various industries. This method facilitates quick design iterations with materials selected specifically to suit each prototype or tool’s requirements.
Why Choose PROTOTEK for CNC milling?

BEST SERVICE

HIGH-PRECISION

PROFESSIONAL TEAM
Choosing Prototek for your CNC milling project means leveraging our extensive range of services, which are designed to support you at every step. Our cutting-edge equipment ensures parts are machined with exquisite precision and within tight tolerances, guaranteeing top-tier accuracy and quality throughout fabrication. Our experienced engineers and technicians offer outstanding guidance and support from start to finish – while our fast turnaround times enable you to meet even tight deadlines! With Prototek’s commitment to customer service excellence and dedication to quality, we make ourselves a reliable and high-quality partner for all your CNC milling needs!

Let's Start Project!
We will give you a quick reply and quote within 12 hours.
- Phone: 0086-18779223927
- Email: Lynnyao@prototekparts.com
- Address: Nanchang,Jiangxi,China
























































