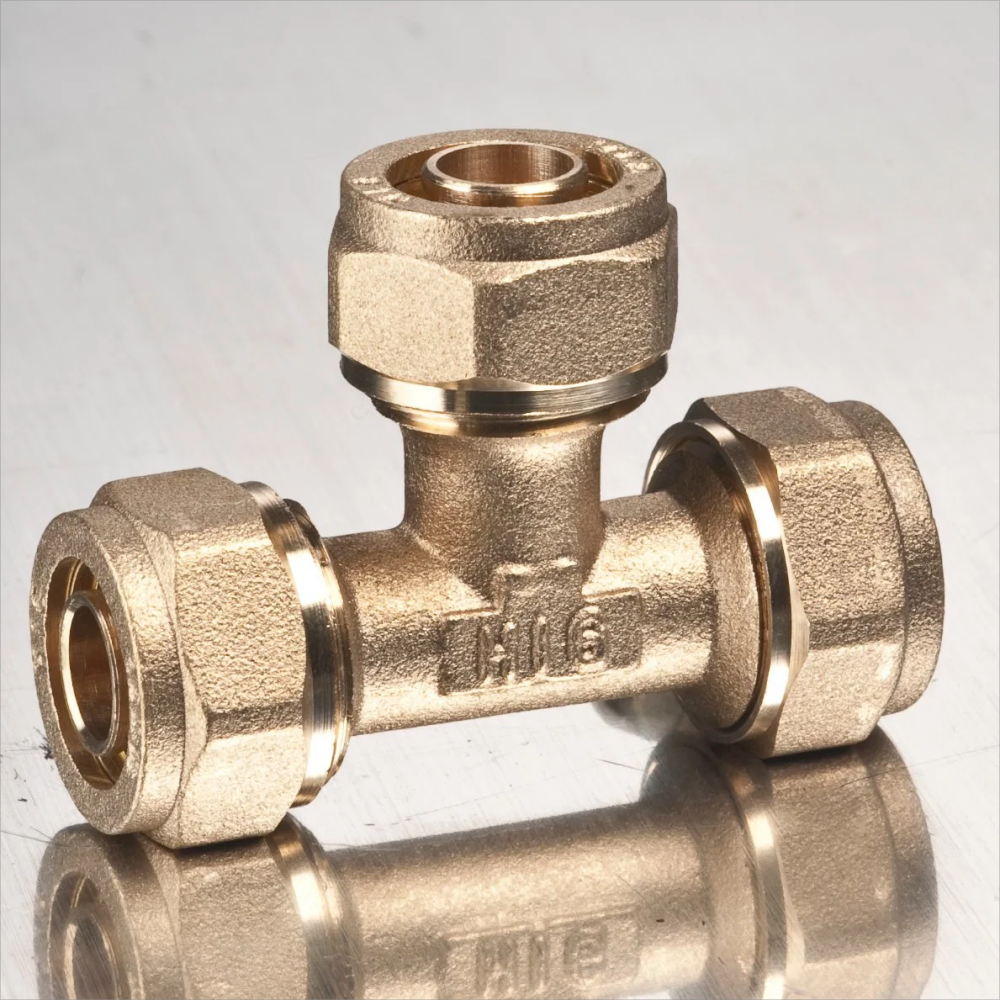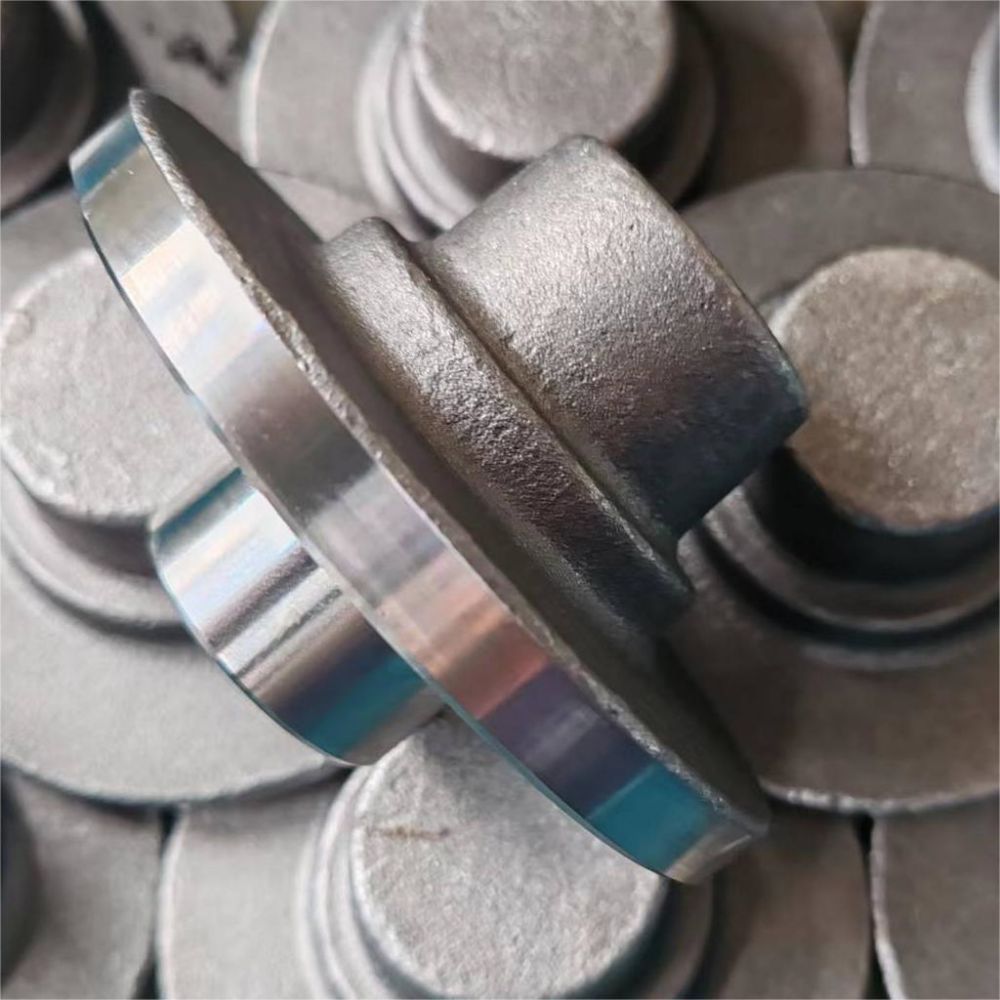
What is Silicone Casting
Silicone casting involves creating molds from silicone rubber to replicate detailed shapes and textures. Unlike traditional casting methods that may require more rigid molds and extensive setup, silicone casting offers flexibility and precision, making it ideal for complex designs and prototypes.
How silicone Casting works?

The process begins with the creation of a master model, which serves as the original prototype or pattern for the final part. This master model can be made from various materials such as clay, wax, resin, or even existing objects that need replication. The master model must accurately represent the final part’s desired shape and surface details.
Once the master model is ready, it is prepared for molding. The master model is placed in a container or frame to contain the liquid silicone rubber. Depending on the complexity of the mold and the desired outcome, mold-making techniques may vary. The container must be adequately sealed to prevent leakage of the silicone material.
Silicone rubber, in the form of liquid silicone rubber (LSR) or room temperature vulcanization (RTV) silicone, is carefully mixed and poured over the master model. LSR is injected into a closed mold to avoid air entrapment and ensure uniformity. RTV silicone, on the other hand, cures at room temperature and is suitable for simpler molds.
After the silicone material is poured over the master model, it undergoes a curing process. This process allows the silicone rubber to solidify and take the shape of the master model. The curing time can vary depending on the type of silicone used, ranging from a few hours to overnight.
Once the silicone has fully cured, the mold is carefully opened, and the master model is removed. This reveals a precise negative impression or cavity within the silicone mold that mirrors the original shape and surface details of the master model.
With the silicone mold prepared, it is now ready for casting parts. Various materials such as polyurethane, epoxy resins, or even liquid metals can be poured or injected into the silicone mold cavity. The mold is closed and secured to prevent leakage during the casting process.
7. Demolding and Finishing
Once the casting material has cured or solidified within the silicone mold, the mold is opened, and the newly formed part is carefully removed. Depending on the application requirements, the part may undergo additional finishing processes such as trimming, sanding, painting, or surface treatments to achieve the desired final appearance and functionality.
Advantages of Silicone Casting
Precision and Detail Preservation
Silicone molds faithfully replicate intricate details and surface textures from the master model.
Flexibility and Durability
Silicone molds can be used repeatedly without significant degradation, making them ideal for both prototyping and production runs.

Veelzijdigheid
Silicone casting accommodates a wide range of materials for casting, allowing for the production of parts with varying mechanical properties and finishes.
Materials Selection for Silicone Casting
Choosing the right materials is crucial in silicone casting to ensure the desired properties and performance of the final parts. While silicone casting is versatile with various materials, including polymers and even some metals, selecting metals requires consideration of their compatibility with silicone molds and casting processes.
Suitable Metal Materials for Silicone Casting
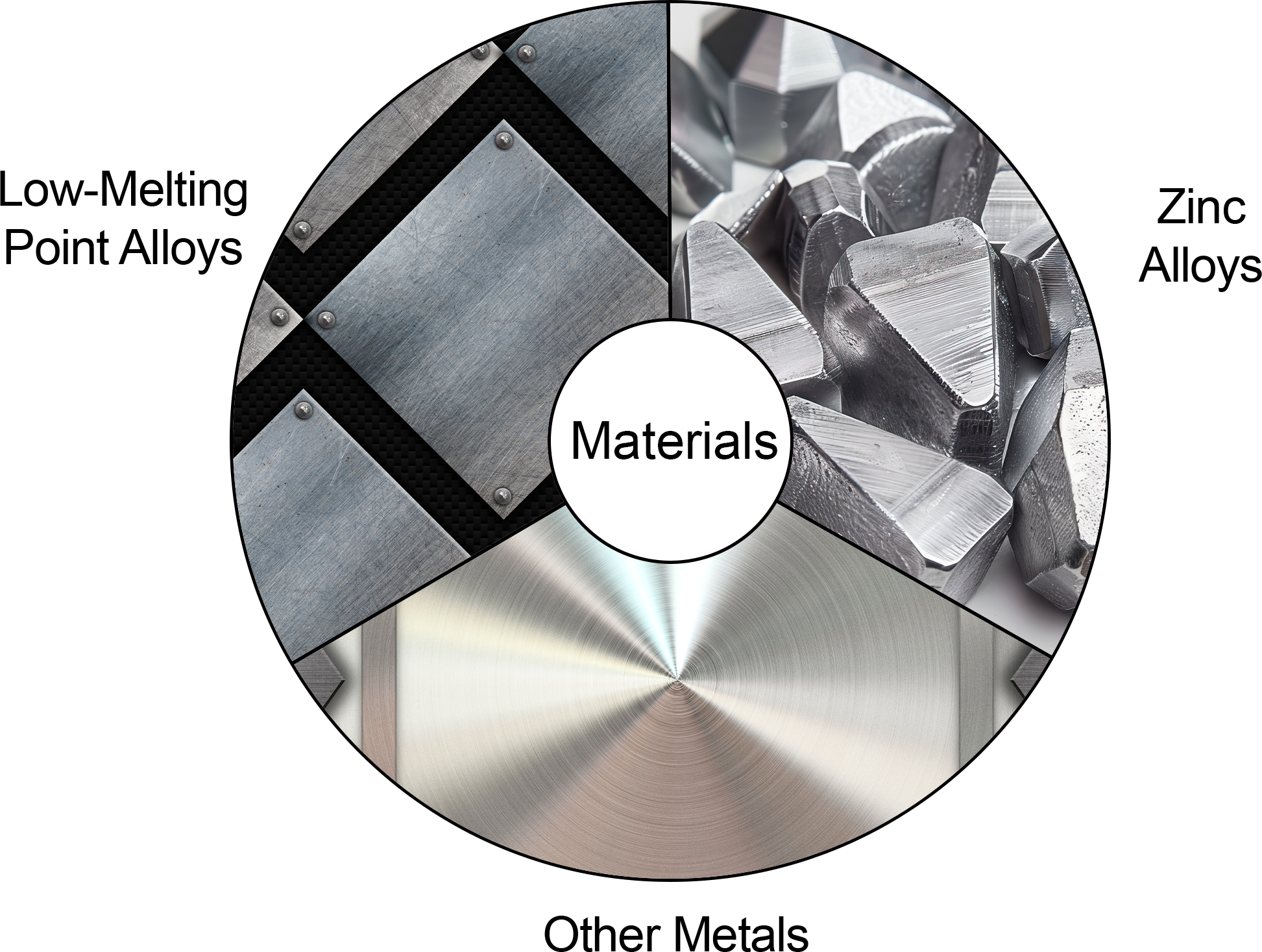
Low-Melting Point Alloys:
- Tin-Based Alloys: Such as pewter, which have low melting points (around 170-230°C), making them ideal for casting into silicone molds without damaging the mold.
- Lead-Based Alloys: Like lead-tin alloys, which are also low melting and suitable for silicone casting.
Zinc Alloys:
- Zamak (Zinc-Aluminum-Magnesium-Copper Alloy): Often used in die casting, Zamak alloys can be cast into silicone molds due to their relatively low melting point (around 380-390°C).
- Other Zinc Alloys: Various other zinc alloys with lower melting temperatures compared to aluminum or brass alloys can also be suitable.
Other Metals:
- Bismuth Alloys: Such as bismuth-tin alloys, which have low melting points (around 140-180°C) and are used in applications requiring low toxicity and high density.
- Indium and Gallium Alloys: These alloys have very low melting points (below 100°C) and are suitable for specialized applications where low-temperature casting is required.
Importance of Surface Treatment

- Melting Point:
Metals with low melting points are generally preferred for silicone casting to prevent damage to the silicone molds during casting. - Pourability and Fluidity:
Metals should have good flow characteristics when molten to ensure complete filling of complex mold cavities and intricate details. - Compatibility with Silicone:
Some metals may react with silicone materials, affecting mold longevity or part quality. Testing compatibility and using suitable release agents are essential.
Surface Treatment in Silicone Casting
Common Surface Treatment Methods

Polishing:
- Mechanical Polishing: Using abrasives such as sandpaper, polishing wheels, or compounds to achieve smooth and glossy surfaces.
- Chemical Polishing: Chemical agents or solutions can be used to dissolve minor imperfections or rough surfaces, followed by buffing to achieve a polished finish.

Coatings and Finishes:
- Painting: Applying paints or coatings to enhance aesthetics or provide specific properties like UV resistance or corrosion protection.
- Clear Coatings: Clear coatings such as varnish or clear epoxy can be applied to preserve the natural appearance of materials like metals or enhance their durability.
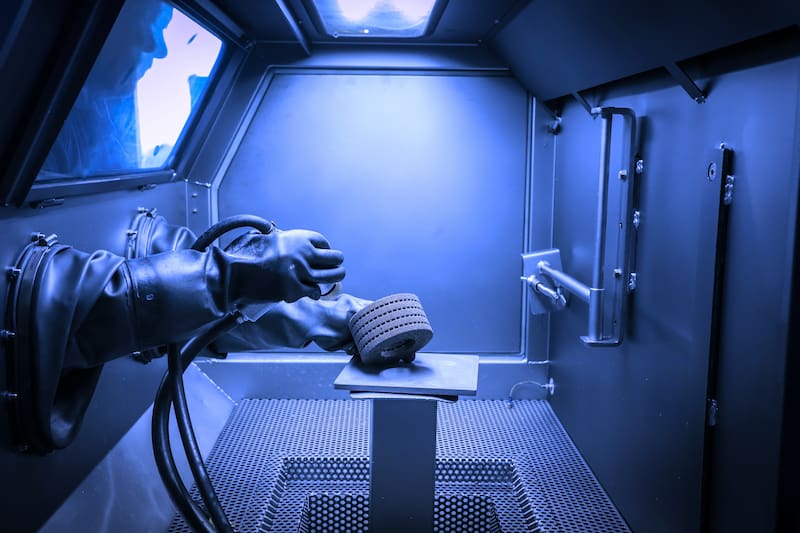

Texturing:
- Sandblasting: Propelling abrasive particles against the surface to create a matte or textured finish, ideal for creating grip surfaces or decorative patterns.
- Etching: Chemical etching can be used to selectively remove material from the surface, creating patterns or improving adhesion for subsequent coatings.
Industry Applications of Silicone Casting
Silicone casting is a versatile manufacturing process that finds extensive use across diverse industries due to its ability to replicate intricate details, customize designs, and facilitate rapid prototyping. Here’s a detailed look at its applications in different sectors:
1. Art and Sculpture
- Art Reproduction: Artists use silicone casting to replicate sculptures and artworks with high fidelity, preserving intricate details and textures.
- Mixed Media Art: Combining silicone casting with other materials allows artists to create mixed-media artworks that blend different textures and finishes.
2. Medical and Dental
- Prosthetics: Silicone casting is used to create custom prosthetic limbs and orthotic devices tailored to individual patient needs.
- Medical Models: Silicone casting produces anatomical models used for surgical planning, training, and patient education in medical and dental fields.
3. Consumer Products
- Decorative Items: Silicone casting is employed in creating decorative figurines, ornaments, and jewelry pieces with intricate designs and textures.
- Household Goods: Production of functional household items such as kitchenware and personal accessories using silicone casting techniques.
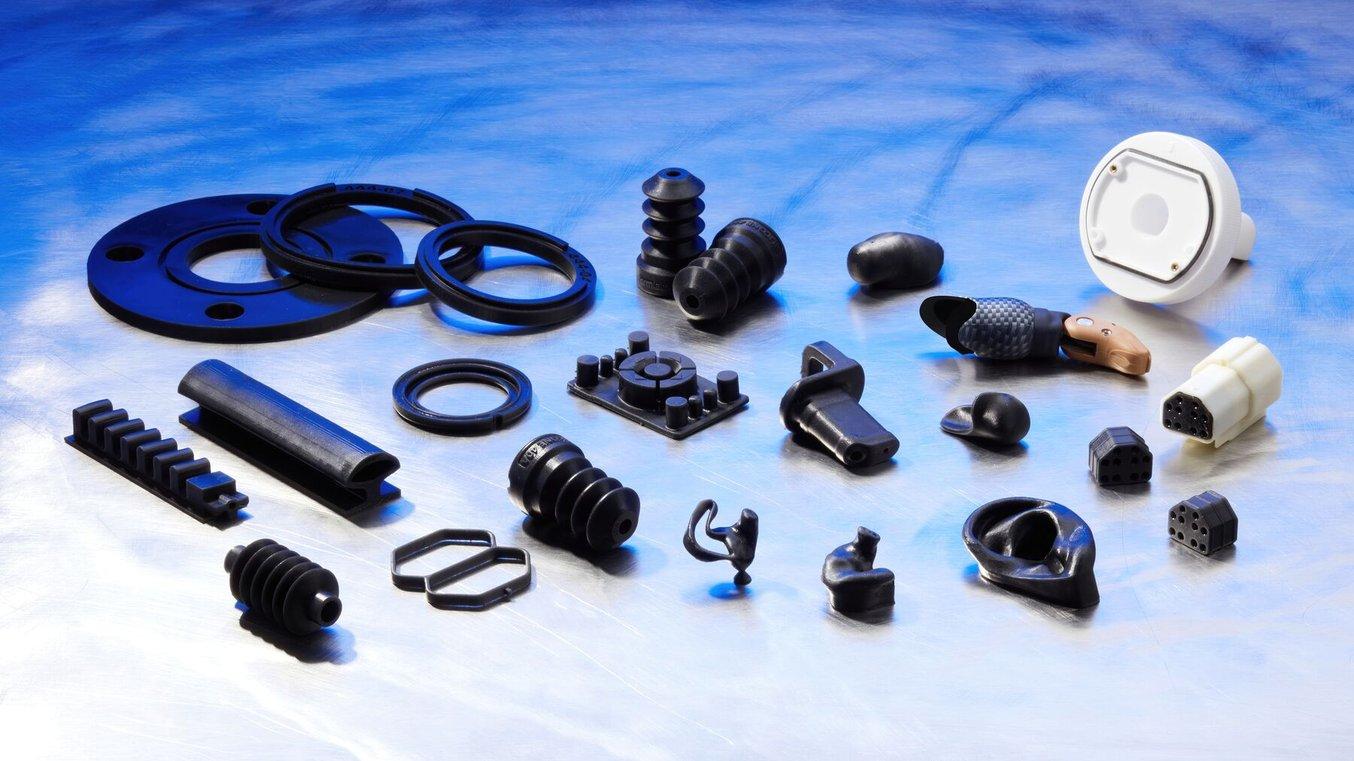

4. Industrial Components
- Replacement Parts: Silicone casting allows for the cost-effective production of replacement parts for industrial machinery and equipment.
- Prototyping: Engineers use silicone casting to create prototypes of mechanical components and assemblies for iterative design refinement.
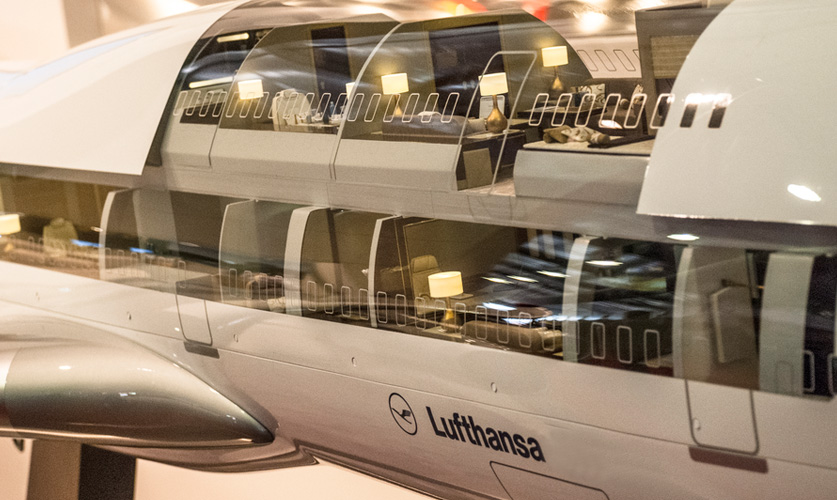

5. Automotive and Aerospace
- Custom Parts: Silicone casting is used in manufacturing custom automotive parts, including interior trim pieces, emblems, and specialty components.
- Prototyping in Aerospace: Aerospace industries utilize silicone casting for prototyping aircraft components and creating tooling molds.
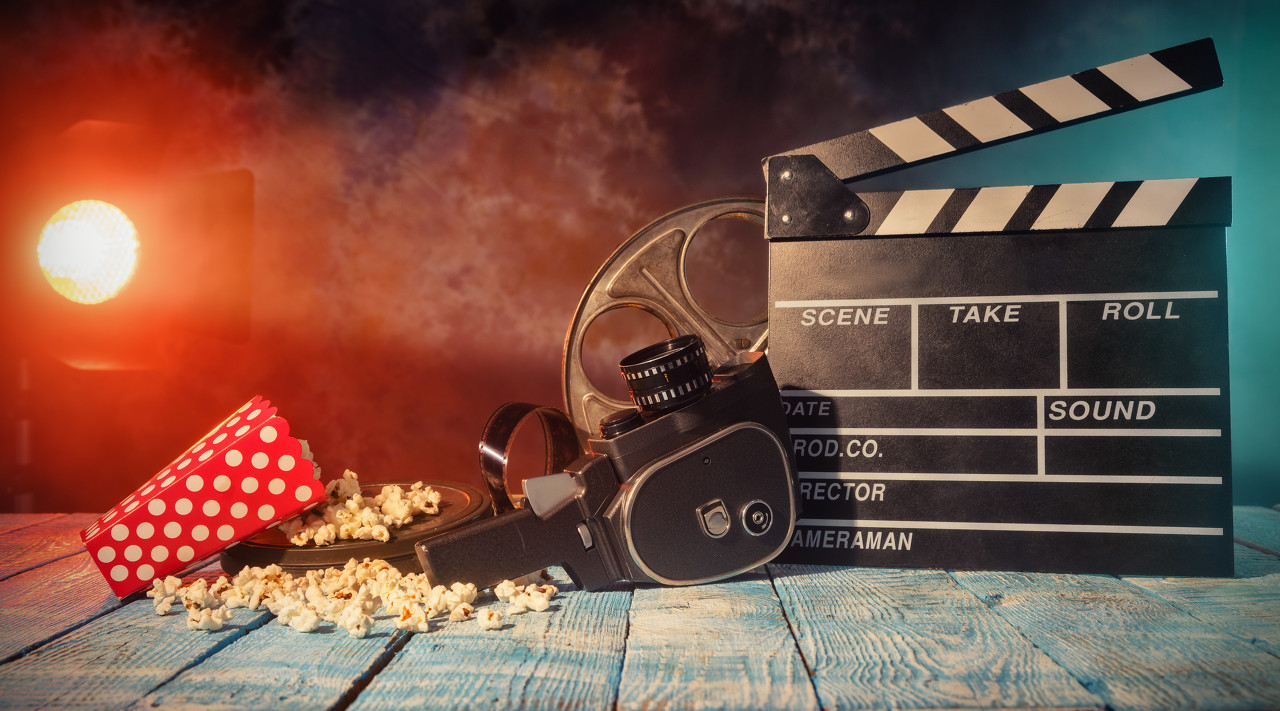

6. Film and Entertainment
- Special Effects: Silicone casting is integral to creating props, costumes, and special effects for film, television, and theater productions.
- Miniatures and Models: Production of detailed miniatures and scale models used in filmmaking, gaming, and museum exhibits.

7. Educational and Research
- Scientific Models: Silicone casting supports the production of scientific models and specimens used in educational settings and research laboratories.
- Experimental Setups: Researchers use silicone casting to create customized experimental setups and apparatus for scientific experiments.

8. Architecture and Design
- Architectural Models: Silicone casting produces detailed architectural models used for visualizing building designs and urban planning.
- Interior Design: Customized decorative elements and prototypes for interior design projects using silicone casting techniques.

9. Jewelry and Fashion
- Custom Jewelry: Artisans use silicone casting to create intricate and personalized jewelry designs with precise detailing.
- Fashion Accessories: Production of unique fashion accessories and embellishments using silicone casting for artistic expression.

10. Sports and Recreation
- Sporting Equipment: Silicone casting is utilized in manufacturing specialized sporting equipment and gear, ensuring durability and performance.
- Recreational Products: Production of recreational items such as toys, hobbyist models, and gaming accessories using silicone casting methods.

Let's Start Project!
We will give you a quick reply and quote within 12 hours.
- Phone: 0086-18779223927
- Email: Lynnyao@prototekparts.com
- Address: Nanchang,Jiangxi,China
























































